overview
PaMS
Panel Method Solver

PaMS code is a 3D low-order unsteady Boundary Element Method for the solution of ideal flows
(inviscid, incompressible and irrotational) with a numerical methodology based on the third
Green’s Identity and the Morino’s formulation.
Main features and capabilities:
Work in progress: non linear water-air free surface.
Future improvement: laminar/turbulent boundary layer, separated flows.
Main features and capabilities:
- external and internal flows;
- unstructured mesh allowed (both tria and quad elements);
- single and multibody simulations (both thick and thin bodies);
- fixed and calculated body motion and/or deformation;
- time marching vorton and doublet free trailing edge wake;
- computation of pressure directly in both control points and grid points;
- treatment of the intersections between two or more bodies;
- wake-body aerodynamic interference;
- compressibility correction.
Work in progress: non linear water-air free surface.
Future improvement: laminar/turbulent boundary layer, separated flows.
The code has been developed in order to have satisfactory analyses and design tool, focusing on a drastic reduction of the costs, in terms of
overall time, resources and man power, by using unstructured grid with both quadrilateral and triangular panels, and by introducing a wide variety
of boundary and closure conditions to perform a variety of aeronautical and naval fluiddynamic time-dependent calculations.
These characteristics permit a greater simplicity and rapidity during the paneling without alteration of the result accuracy, permitting to improve the quality of the discretization of the bodies and to use a numerical representation of CAD designs, making unnecessary the steps consisting in the geometry treatment and paneling as a satisfactory acceptable CAD model is available.
Another simplification for the geometry treatment and paneling is an option for the treatment of eventual intersections between two or more bodies, which consents to panel separately different parts of a same ensemble (for example the wing-fuselage group of an airplane) and to reposition these parts on the basis of specific needs.
Moreover, due to capacity to manage possible deformation of the bodies in time, it is simple to use the PaMS code to do also unsteady computations of fluid-structure interactions, as in the case of aeroelastic problems (like the sails), putting in new routines for the structural test or utilizing the coupling with commercial softwares.
The possibility to interface directly with the most diffuse commercial softwares (Gambit, Nastran, Hypermesh, Tecplot, ParaView) consents to utilize at one’s best the approximatively developed codes and the codes dedicated to these operations putting the PaMS code in ideal conditions to increase its performances.
This method has been used to solve a number of scientific and technical, steady and unsteady problems.
These characteristics permit a greater simplicity and rapidity during the paneling without alteration of the result accuracy, permitting to improve the quality of the discretization of the bodies and to use a numerical representation of CAD designs, making unnecessary the steps consisting in the geometry treatment and paneling as a satisfactory acceptable CAD model is available.
Another simplification for the geometry treatment and paneling is an option for the treatment of eventual intersections between two or more bodies, which consents to panel separately different parts of a same ensemble (for example the wing-fuselage group of an airplane) and to reposition these parts on the basis of specific needs.
Moreover, due to capacity to manage possible deformation of the bodies in time, it is simple to use the PaMS code to do also unsteady computations of fluid-structure interactions, as in the case of aeroelastic problems (like the sails), putting in new routines for the structural test or utilizing the coupling with commercial softwares.
The possibility to interface directly with the most diffuse commercial softwares (Gambit, Nastran, Hypermesh, Tecplot, ParaView) consents to utilize at one’s best the approximatively developed codes and the codes dedicated to these operations putting the PaMS code in ideal conditions to increase its performances.
This method has been used to solve a number of scientific and technical, steady and unsteady problems.

governing equations
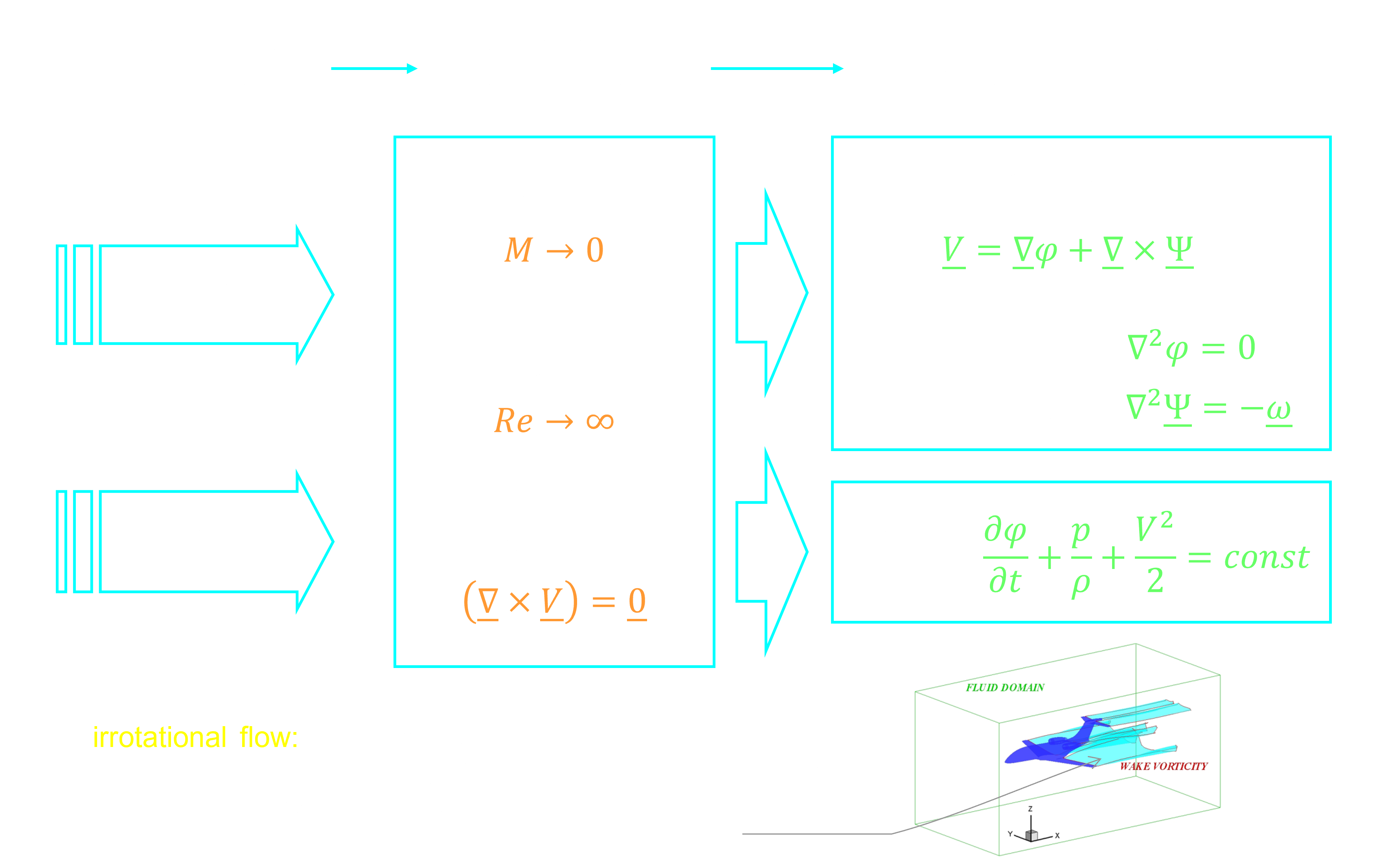
Laplace equation solution
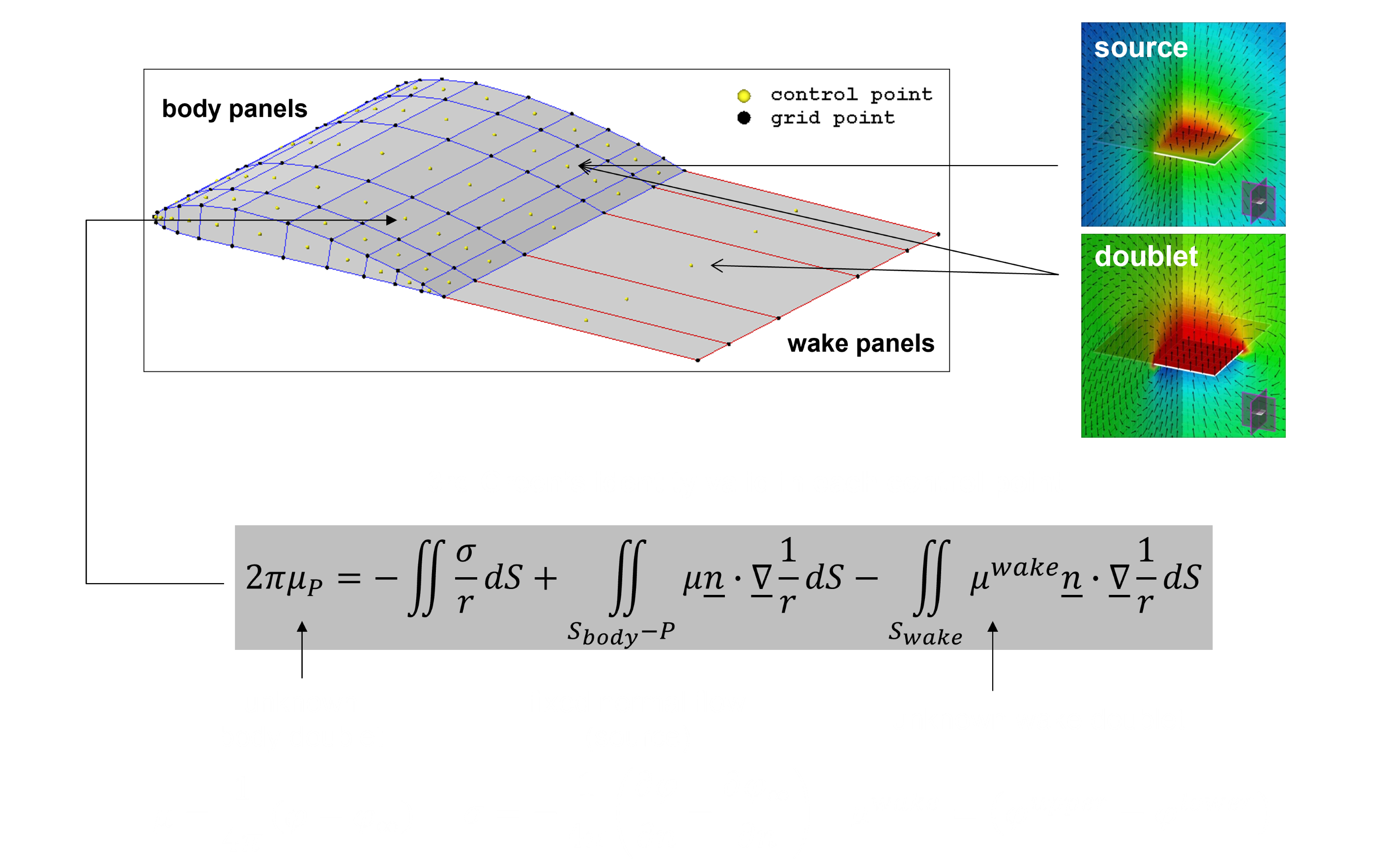
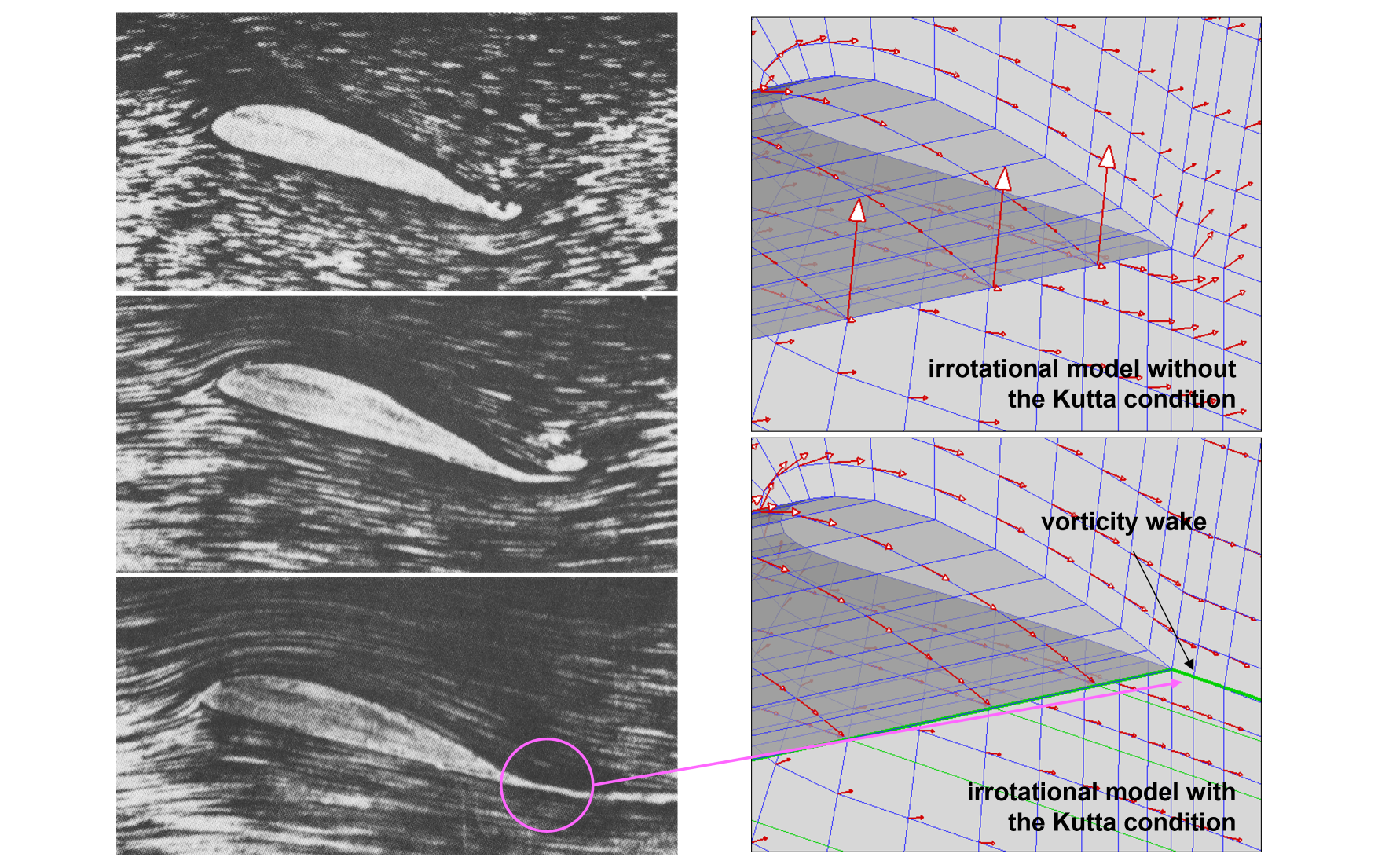
Kutta condition
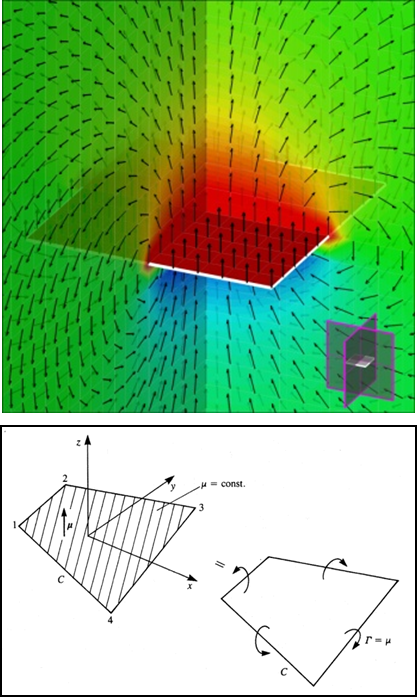
tip vortex and doublet-vortex ring equivalence
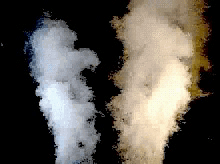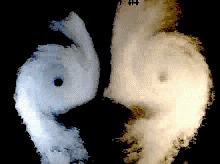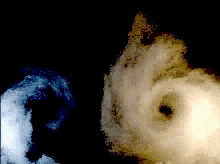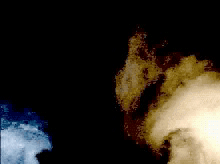
conversion doublet-vortons
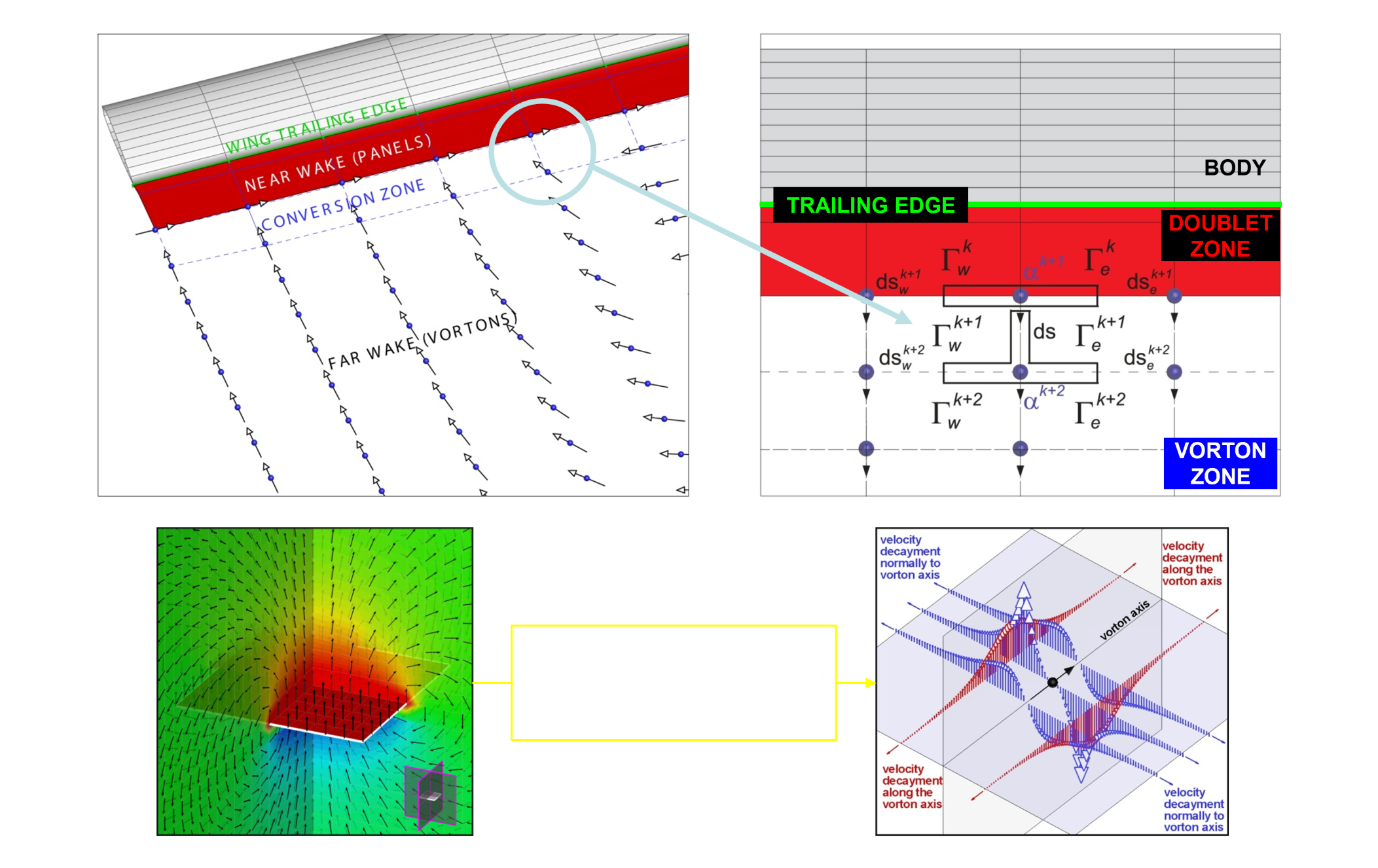
doublets vs vortons (rotor in hover)
classical doublet wakes can be difficult (or impossible) to manage...

...vortons are easier to manage
